Освещение высоких и низких пролетов: в чем реальная разница?

Введение
Если вы когда-нибудь смотрели на потолок своего завода и задавались вопросом: «Почему там так много разных светильников?», вы не одиноки. Споры о том, какое освещение лучше использовать: для высоких и низких складов, озадачивали многих управляющих складами и подрядчиков.
Подумайте об этом так: светильники для высоких пролётов — это мощные прожекторы промышленного мира, созданные для освещения с потолка. Светильники для низких пролётов, с другой стороны, — их более практичные собратья, идеально подходящие для пространств, где не требуется высокое освещение.
В этом руководстве мы разберем, чем отличаются эти два типа освещения, где каждый из них подходит лучше всего и почему современные светодиодные технологии меняют правила игры к лучшему.
Оглавление
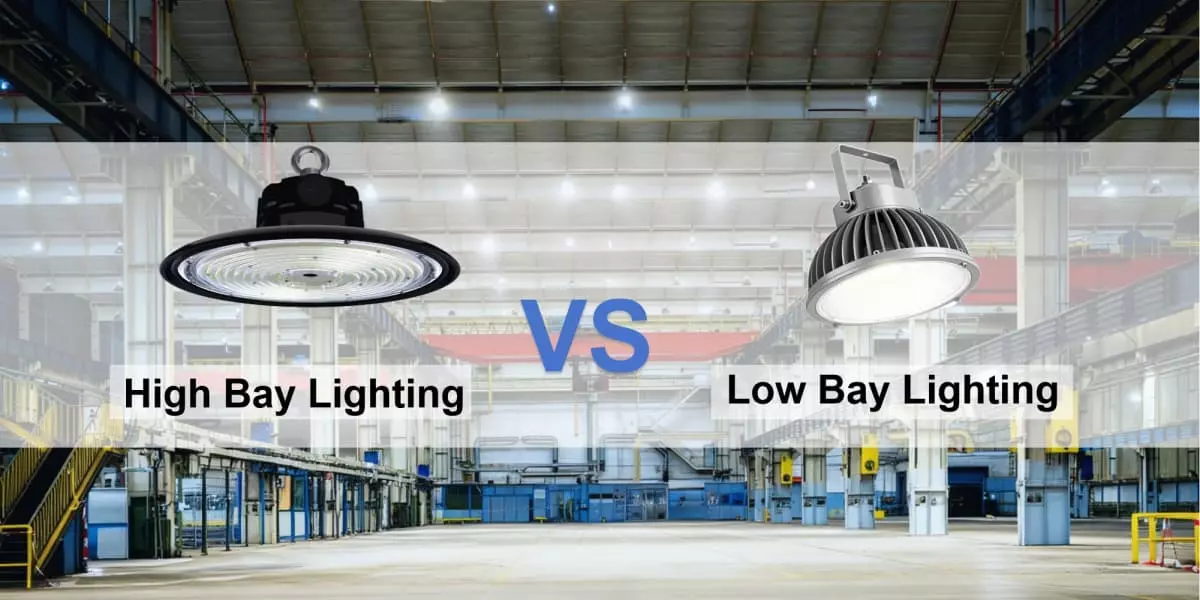
В чем разница между освещением высоких и низких пролетов?
Светодиодное или люминесцентное освещение: какое лучше?
Светодиодные светильники для высоких и низких пролетов
Что выбрать — High Bay или Low Bay?
Как выбрать правильное освещение пролета для вашего объекта?
Почему светодиодные прожекторы — это будущее промышленного освещения?
Что такое освещение пролётов?
Освещение пролётов относится к системам освещения, предназначенным для больших открытых закрытых помещений , таких как фабрики, склады, спортзалы и крупные розничные магазины. Эти зоны требуют яркого и равномерного освещения, чтобы работники могли хорошо видеть, безопасно передвигаться и поддерживать производительность труда.
Проще говоря, освещение пролётов делится на два типа в зависимости от высоты потолка :
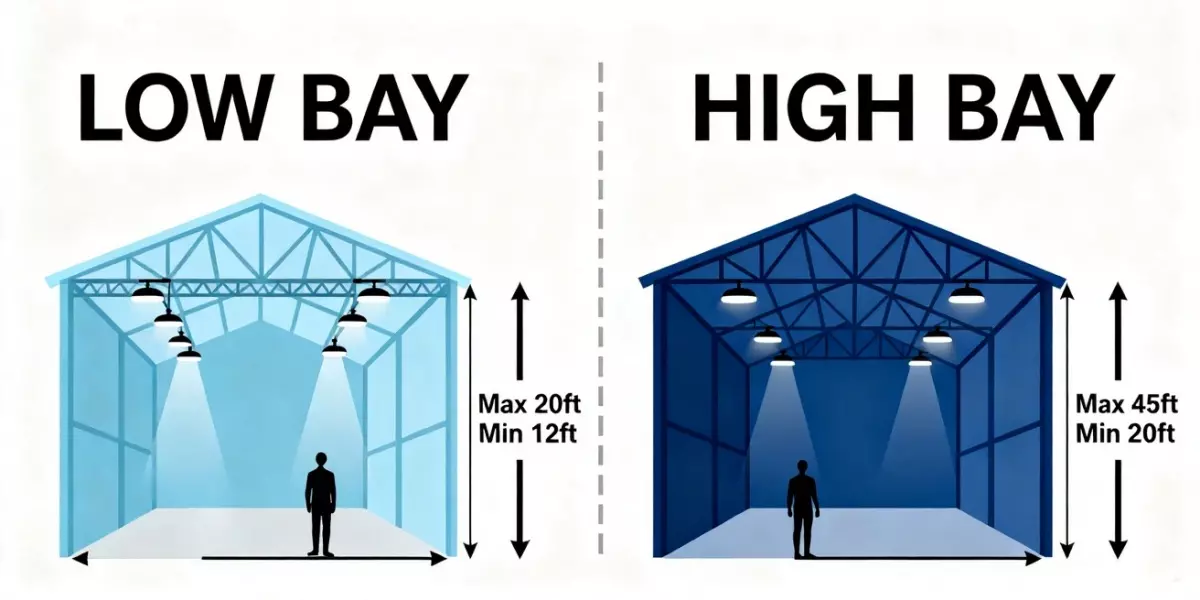
Освещение высоких пролетов — используется для потолков высотой более 20 футов.
Освещение для низких пролетов — используется для потолков ниже 20 футов.
Эта разница имеет значение, поскольку чем выше потолок, тем сильнее и уже должен быть луч, чтобы обеспечить достаточное освещение пола.
Раньше на многих объектах использовались металлогалогенные или люминесцентные светильники.
Сегодня светодиодное освещение стало стандартом благодаря своей энергоэффективности, длительному сроку службы и стабильной яркости. Оно обеспечивает надёжное и неприхотливое освещение для любых промышленных и коммерческих помещений.
В чем разница между освещением высоких и низких пролетов?
Понимание разницы между освещением для высоких и низких пролётов крайне важно при проектировании освещения промышленных или коммерческих помещений. Оба типа освещения предназначены для больших помещений, но их конфигурация и характеристики различаются в зависимости от высоты потолка, необходимой яркости и распределения светового потока.
(1) Высота установки
Первый и самый важный фактор — высота потолка .
Светильники для высоких пролётов предназначены для потолков высотой более 6 метров (20 футов) . Они обеспечивают мощный, сфокусированный свет, достигающий пола без потери яркости.
Низкие светильники лучше всего подходят для потолков ниже 6 метров . Они рассеивают свет шире, предотвращая появление слишком ярких пятен и бликов.
Выбор неправильного типа может привести к потере энергии или неравномерному освещению.
(2) Применение
Освещение высоких пролетов обычно используется на складах, в производственных цехах, авиационных ангарах и спортивных аренах — в любых помещениях с высокими потолками и большим вертикальным пространством.
Низкоуровневое освещение подходит для мастерских, розничных магазинов, гаражей и сборочных цехов , где потолки ниже и работникам требуется более мягкое и широкое освещение.
Правильное сочетание повышает как безопасность, так и видимость повседневной работы.
(3) Угол луча
Конструкция балки также разделяет эти два типа.
Светильники для высоких пролетов используют более узкие лучи (60°–90°), чтобы направлять свет дальше вниз.
Светильники для низких пролетов имеют более широкие лучи (100°–120°), что позволяет равномерно распределять свет на небольшой высоте.
Это обеспечивает равномерную яркость во всем рабочем пространстве.
(4) Монтаж
Светильники для высоких пролётов обычно подвешиваются на цепях, крюках или подвесах , в то время как светильники для низких пролётов часто монтируются на поверхности или подвешиваются на более коротких расстояниях . Способ крепления помогает контролировать рассеивание света и облегчает доступ к обслуживанию.
(5) Мощность и световой поток
Разница в производительности очевидна в цифрах:
Высокие светильники : 150–400 Вт, световой поток около 15 000–40 000 люмен .
Низкий пролет : 60–150 Вт, световой поток около 6000–15000 люмен .
Подводя итог: освещение в высоких пролётах фокусирует свет с большей высоты; освещение в низких пролётах рассеивает его ближе к земле. Понимание этого различия позволит вам выбрать правильный светильник для оптимальной эффективности и комфорта в вашем помещении.
Светодиодное или люминесцентное освещение: какое лучше?
Сравнивая светодиодные и люминесцентные светильники , можно увидеть очевидную разницу в производительности и долгосрочной ценности. Светодиоды быстро стали предпочтительным выбором для заводов, складов и мастерских по всей Европе и США.
Энергоэффективность
Светодиодные светильники для освещения пролётов потребляют до 70% меньше энергии , чем люминесцентные, обеспечивая при этом такую же или более высокую яркость. Это означает снижение расходов на электроэнергию и уменьшение выбросов углекислого газа — важные преимущества для современных промышленных предприятий.
Яркость и качество
Светодиоды обеспечивают равномерное освещение без мерцания и улучшенную цветопередачу. Работники могут более точно различать детали и цвета, что повышает безопасность и производительность. Флуоресцентные лампы, напротив, со временем мерцают, выцветают и теряют яркость.
Техническое обслуживание и срок службы
A quality LED bay fixture can last 50,000 hours or more, often five times longer than fluorescent tubes. There are no ballasts to replace and no fragile glass to handle.
Instant-On & Control
LEDs turn on instantly and integrate easily with motion sensors or smart controls, something fluorescent lights can’t do effectively.
For these reasons, LEDs dominate industrial retrofits — offering stronger light, lower costs, and less downtime for maintenance.
High Bay LED Lights vs Low Bay LED Lights
When both lighting types move into the LED era, the difference between high bay LED lights vs low bay LED lights becomes more about engineering design than basic height or brightness.
Optical Design
LED technology allows light to be shaped with precision lenses rather than old-style reflectors.
High bay LEDs use narrow, high-intensity lenses to push light down from 20–50 feet, ensuring uniform brightness across tall spaces.
Low bay LEDs use wider beam optics to cover shorter distances with softer, more comfortable light.
This optical control reduces glare and improves energy efficiency per lumen.
Heat Dissipation
Because high bay fixtures run at higher wattages, they require larger aluminum heat sinks or active cooling designs to protect LED chips. Low bay units generate less heat, so they often feature compact passive cooling that keeps fixtures lighter and easier to mount.
Smart Controls & Integration
Modern industrial LED lighting supports motion sensors, daylight harvesting, and IoT control systems. High bay models often use networked or wireless systems for energy savings in warehouses, while low bay lights integrate simple occupancy sensors for smaller areas.
Efficiency & Reliability
Both types now exceed 150 lumens per watt, offering powerful, consistent light with minimal maintenance.
Ceramiclite provides high bay LED lighting solutions designed for industrial environments — combining optical precision, durable materials, and smart control compatibility to meet diverse facility needs.
Which Should You Choose — High Bay or Low Bay?
Now that we've outlined the key differences, you're probably wondering: "So which one is right for MY space?" The right choice boils down to your ceiling height, lighting needs, and work environment.
Instead of getting lost in the details, use the quick-reference guide below to make an initial determination.
The right choice depends on your ceiling height, lighting needs, and work environment. Each type serves a specific purpose, and picking the right one ensures both efficiency and comfort.
Here’s a quick guide to help you decide:
Condition | Recommended Lighting | Reason |
Ceiling above 20 ft (6 m) | High Bay | Delivers concentrated brightness with a narrow beam angle to reach the floor evenly. |
Ceiling below 20 ft | Low Bay | Offers a wider beam for softer, more diffused light. |
Warehouses / factories / gymnasiums | High Bay | Designed for high illumination intensity and large spaces. |
Retail stores / garages / workshops | Low Bay | Provides balanced brightness and better visual comfort for smaller areas. |
Tip: When in doubt, choose based on your lux requirement — high bay for power, low bay for comfort.
For a more detailed analysis of each factor—like calculating exact brightness needs or selecting the perfect beam angle—continue to the next section, where we break down the complete selection process.
How to Choose the Right Bay Lighting for Your Facility?
Selecting the right fixture can make or break your lighting performance. When you choose the right bay lighting, the goal is simple — achieve consistent brightness, reduce energy costs, and maintain long-term reliability. Here’s a quick guide to help you decide.
(1) Beam Angle and Width
Start with your ceiling height.
For ceilings above 20 ft, use narrower beams (60°–90°) to concentrate light on the work floor.
For ceilings below 20 ft, choose wider beams (100°–120°) for smoother, more even coverage.
This ensures your light reaches the right area without glare or dark spots.
(2) Mounting & Distribution
Consider your mounting options: chain, pendant, or surface mount.
High bay fixtures are often suspended to control light spread.
Low bay fixtures can be surface-mounted for a cleaner look.
Proper mounting height directly affects light distribution and maintenance access.
(3) Retrofitting Existing Fixtures
If your facility already uses older metal halide or fluorescent lights, LED retrofits are the fastest way to cut energy use and improve brightness. They fit existing mounts, minimizing installation cost and downtime.
(4) Power & Brightness
Use lumens per square foot as your guide:
Storage areas: 10–20 lm/ft²
Assembly or production: 30–50 lm/ft²
Inspection zones: 70+ lm/ft²
Focus on lumen output, not just wattage, to ensure efficient lighting design.
(5) Color Temperature
A neutral white tone between 4000K and 5000K gives the best visibility for industrial work. It reduces eye strain and enhances material contrast.
(6) Shape: UFO vs Linear Fixtures
UFO high bay lights deliver strong, centralized illumination — ideal for large, open areas.
Linear low bay lights spread light evenly across aisles or production lines, perfect for lower ceilings and rectangular layouts.
Visualizing this helps match fixture shape with your room geometry.
(7) Energy Usage & ROI
Calculate your return on investment (ROI) based on energy savings, lifespan, and reduced maintenance. Most LED systems pay for themselves within 1–2 years, then continue saving for over a decade.
By following these steps, facility managers and engineers can confidently select lighting that improves safety, productivity, and energy efficiency — all while ensuring the best long-term value for their operation.
Why LED Bay Lights Are the Future of Industrial Lighting?
The shift toward LED bay lights is more than a trend — it’s the future of industrial lighting. Across Europe and the US, factories and warehouses are moving away from traditional fixtures to smarter, more efficient LED systems that support long-term sustainability goals.
Modern LED bay lights do more than just illuminate. They connect. Integrated motion sensors, daylight harvesting, and IoT controls allow lights to adjust automatically based on occupancy or ambient light levels. This reduces wasted energy and extends fixture lifespan while keeping workspaces consistently bright and safe.
Governments and corporations are also driving change. Energy-efficiency standards and ESG requirements now encourage facilities to cut power use and carbon emissions. LEDs make compliance simple — delivering high output with low consumption.
Looking ahead, LED lighting will become the backbone of smart, data-driven facilities, where lighting systems communicate with HVAC, security, and production networks.
Ceramiclite’s HB01 High Bay LED bay lights are engineered with these innovations in mind — combining optical precision, smart compatibility, and industrial-grade durability. They’re ready for today’s efficiency demands and tomorrow’s intelligent infrastructure.
Want to know more about What is New in Industrial LED Lighting?
Conclusion
Choosing between high bay vs low bay lighting comes down to three key factors — ceiling height, beam angle, and brightness needs. High bay lights deliver powerful, focused illumination for tall spaces, while low bay lights provide softer, wider coverage for lower ceilings.
Upgrading to LED bay lighting ensures higher efficiency, lower maintenance, and long-term ROI — a smart move for any modern facility.
Всё ещё не уверены, какой вариант подойдёт вашему помещению? Получите бесплатную схему освещения от Ceramiclite уже сегодня и найдите идеальный баланс производительности, экономичности и надёжности для вашей промышленной среды.
_thumb.jpg)