Iluminación para naves industriales altas frente a iluminación para naves industriales bajas: ¿Cuál es la diferencia real?

Introducción
Si alguna vez te has quedado mirando el techo de tu fábrica preguntándote: "¿Por qué hay tantos tipos de luces ahí arriba?", no estás solo. El debate entre la iluminación para naves industriales altas y bajas ha desconcertado a más de un gerente de almacén y contratista.
Piénsalo así: las luminarias de gran altura son como los potentes reflectores del mundo industrial, diseñadas para iluminar desde lo más alto. Las luminarias de baja altura, en cambio, son sus primas más prácticas, perfectas para espacios que no necesitan una iluminación tan intensa.
En esta guía, analizaremos en detalle las diferencias entre estos dos tipos de iluminación, dónde encaja mejor cada uno y por qué la moderna tecnología LED está cambiando las reglas del juego para siempre.
Tabla de contenido
¿Cuál es la diferencia entre la iluminación para naves industriales altas y bajas?
Iluminación LED frente a iluminación fluorescente para bahías: ¿Cuál funciona mejor?
Luces LED de gran altura frente a luces LED de baja altura
¿Cuál debería elegir: naves industriales altas o naves industriales bajas?
¿Cómo elegir la iluminación adecuada para su instalación?
¿Por qué las luminarias LED para bahías son el futuro de la iluminación industrial?
¿Qué es Bay Lighting?
La iluminación de bahías se refiere a los sistemas de iluminación diseñados para grandes espacios interiores abiertos , como fábricas, almacenes, gimnasios y grandes superficies comerciales. Estas áreas requieren una iluminación brillante y uniforme para que los trabajadores puedan ver con claridad, moverse con seguridad y mantener la productividad.
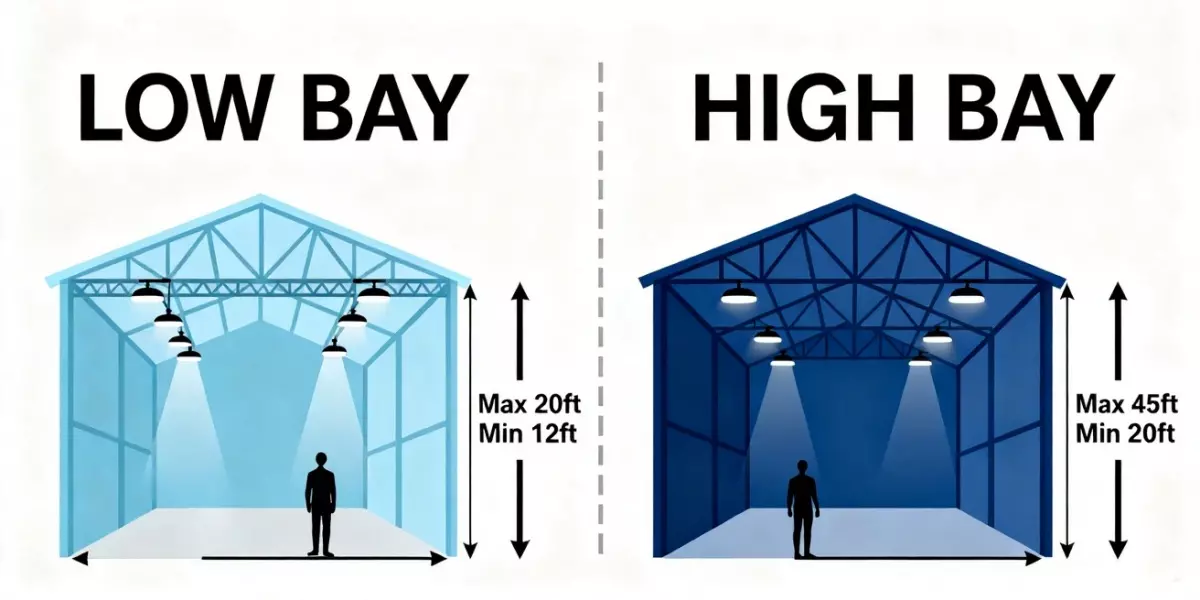
En términos sencillos, la iluminación de bahías se divide en dos tipos según la altura del techo :
Iluminación de gran altura – utilizada para techos de más de 20 pies de altura aproximadamente.
Iluminación de baja altura – utilizada para techos de menos de 20 pies aproximadamente.
Esta diferencia es importante porque cuanto más alto sea el techo, más potente y estrecho deberá ser el haz de luz para proporcionar suficiente luz al suelo.
En el pasado, muchas instalaciones utilizaban lámparas de halogenuros metálicos o fluorescentes.
Hoy en día, la iluminación LED para naves industriales se ha convertido en el estándar gracias a su eficiencia energética, larga vida útil y brillo constante. Proporciona una iluminación fiable y de bajo mantenimiento para cualquier espacio industrial o comercial.
¿Cuál es la diferencia entre la iluminación para naves industriales altas y bajas?
Comprender la diferencia entre la iluminación de gran altura y la de baja altura es fundamental al diseñar un plan de iluminación industrial o comercial. Ambas iluminan grandes espacios, pero su configuración y rendimiento varían según la altura del techo, las necesidades de luminosidad y la distribución del haz de luz.
(1) Altura de instalación
El primer factor, y el más importante, es la altura del techo .
Las luminarias de gran altura están diseñadas para techos de más de 6 metros (20 pies) de altura . Proporcionan una luz potente y focalizada que llega hasta el suelo sin perder brillo.
Low bay lights work best for ceilings below 20 feet. They spread light more widely to avoid over-bright spots or glare.
Choosing the wrong type can cause wasted energy or uneven lighting.
(2) Application
High bay lighting is commonly used in warehouses, production halls, aircraft hangars, and sports arenas — any area with tall ceilings and large vertical space.
Low bay lighting fits workshops, retail stores, garages, and assembly rooms, where ceilings are lower and workers need softer, wider illumination.
The right match improves both safety and visibility in daily operations.
(3) Beam Angle
Beam design also separates the two types.
High bay fixtures use narrower beams (60°–90°) to push light farther down.
Low bay fixtures have wider beams (100°–120°) to spread light evenly at lower heights.
This ensures consistent brightness across the workspace.
(4) Mounting
High bay lights are typically hung by chains, hooks, or pendants, while low bay lights are often surface-mounted or suspended at shorter distances. The mounting method helps control light spread and maintenance access.
(5) Wattage & Lumen Output
The performance difference is clear in numbers:
High bay: 150–400W, producing about 15,000–40,000 lumens.
Low bay: 60–150W, producing about 6,000–15,000 lumens.
In summary: high bay lighting focuses light from greater heights; low bay lighting spreads it closer to the ground. Knowing this distinction ensures you select the right fixture for optimal efficiency and comfort in your facility.
LED vs Fluorescent Bay Lighting: Which Performs Better?
When comparing LED bay lights vs fluorescent, the difference in performance and long-term value is clear. LEDs have quickly become the preferred choice for factories, warehouses, and workshops across Europe and the US.
Energy Efficiency
LED bay lights use up to 70% less energy than fluorescent fixtures while producing the same or higher brightness. This means lower electricity bills and smaller carbon footprints — both major advantages for modern industrial facilities.
Brightness & Quality
LEDs provide consistent, flicker-free light with better color rendering. Workers can see details and colors more accurately, improving safety and productivity. Fluorescent lights, in contrast, tend to flicker, fade, and lose brightness over time.
Maintenance & Lifespan
A quality LED bay fixture can last 50,000 hours or more, often five times longer than fluorescent tubes. There are no ballasts to replace and no fragile glass to handle.
Instant-On & Control
LEDs turn on instantly and integrate easily with motion sensors or smart controls, something fluorescent lights can’t do effectively.
For these reasons, LEDs dominate industrial retrofits — offering stronger light, lower costs, and less downtime for maintenance.
High Bay LED Lights vs Low Bay LED Lights
When both lighting types move into the LED era, the difference between high bay LED lights vs low bay LED lights becomes more about engineering design than basic height or brightness.
Optical Design
LED technology allows light to be shaped with precision lenses rather than old-style reflectors.
High bay LEDs use narrow, high-intensity lenses to push light down from 20–50 feet, ensuring uniform brightness across tall spaces.
Low bay LEDs use wider beam optics to cover shorter distances with softer, more comfortable light.
This optical control reduces glare and improves energy efficiency per lumen.
Heat Dissipation
Because high bay fixtures run at higher wattages, they require larger aluminum heat sinks or active cooling designs to protect LED chips. Low bay units generate less heat, so they often feature compact passive cooling that keeps fixtures lighter and easier to mount.
Smart Controls & Integration
Modern industrial LED lighting supports motion sensors, daylight harvesting, and IoT control systems. High bay models often use networked or wireless systems for energy savings in warehouses, while low bay lights integrate simple occupancy sensors for smaller areas.
Efficiency & Reliability
Both types now exceed 150 lumens per watt, offering powerful, consistent light with minimal maintenance.
Ceramiclite provides high bay LED lighting solutions designed for industrial environments — combining optical precision, durable materials, and smart control compatibility to meet diverse facility needs.
Which Should You Choose — High Bay or Low Bay?
Now that we've outlined the key differences, you're probably wondering: "So which one is right for MY space?" The right choice boils down to your ceiling height, lighting needs, and work environment.
Instead of getting lost in the details, use the quick-reference guide below to make an initial determination.
The right choice depends on your ceiling height, lighting needs, and work environment. Each type serves a specific purpose, and picking the right one ensures both efficiency and comfort.
Here’s a quick guide to help you decide:
Condition | Recommended Lighting | Reason |
Ceiling above 20 ft (6 m) | High Bay | Delivers concentrated brightness with a narrow beam angle to reach the floor evenly. |
Ceiling below 20 ft | Low Bay | Offers a wider beam for softer, more diffused light. |
Warehouses / factories / gymnasiums | High Bay | Designed for high illumination intensity and large spaces. |
Retail stores / garages / workshops | Low Bay | Provides balanced brightness and better visual comfort for smaller areas. |
Tip: When in doubt, choose based on your lux requirement — high bay for power, low bay for comfort.
For a more detailed analysis of each factor—like calculating exact brightness needs or selecting the perfect beam angle—continue to the next section, where we break down the complete selection process.
How to Choose the Right Bay Lighting for Your Facility?
Selecting the right fixture can make or break your lighting performance. When you choose the right bay lighting, the goal is simple — achieve consistent brightness, reduce energy costs, and maintain long-term reliability. Here’s a quick guide to help you decide.
(1) Beam Angle and Width
Start with your ceiling height.
For ceilings above 20 ft, use narrower beams (60°–90°) to concentrate light on the work floor.
For ceilings below 20 ft, choose wider beams (100°–120°) for smoother, more even coverage.
This ensures your light reaches the right area without glare or dark spots.
(2) Mounting & Distribution
Consider your mounting options: chain, pendant, or surface mount.
High bay fixtures are often suspended to control light spread.
Low bay fixtures can be surface-mounted for a cleaner look.
Proper mounting height directly affects light distribution and maintenance access.
(3) Retrofitting Existing Fixtures
If your facility already uses older metal halide or fluorescent lights, LED retrofits are the fastest way to cut energy use and improve brightness. They fit existing mounts, minimizing installation cost and downtime.
(4) Power & Brightness
Use lumens per square foot as your guide:
Storage areas: 10–20 lm/ft²
Assembly or production: 30–50 lm/ft²
Inspection zones: 70+ lm/ft²
Focus on lumen output, not just wattage, to ensure efficient lighting design.
(5) Color Temperature
A neutral white tone between 4000K and 5000K gives the best visibility for industrial work. It reduces eye strain and enhances material contrast.
(6) Shape: UFO vs Linear Fixtures
UFO high bay lights deliver strong, centralized illumination — ideal for large, open areas.
Linear low bay lights spread light evenly across aisles or production lines, perfect for lower ceilings and rectangular layouts.
Visualizing this helps match fixture shape with your room geometry.
(7) Energy Usage & ROI
Calculate your return on investment (ROI) based on energy savings, lifespan, and reduced maintenance. Most LED systems pay for themselves within 1–2 years, then continue saving for over a decade.
By following these steps, facility managers and engineers can confidently select lighting that improves safety, productivity, and energy efficiency — all while ensuring the best long-term value for their operation.
Why LED Bay Lights Are the Future of Industrial Lighting?
The shift toward LED bay lights is more than a trend — it’s the future of industrial lighting. Across Europe and the US, factories and warehouses are moving away from traditional fixtures to smarter, more efficient LED systems that support long-term sustainability goals.
Modern LED bay lights do more than just illuminate. They connect. Integrated motion sensors, daylight harvesting, and IoT controls allow lights to adjust automatically based on occupancy or ambient light levels. This reduces wasted energy and extends fixture lifespan while keeping workspaces consistently bright and safe.
Governments and corporations are also driving change. Energy-efficiency standards and ESG requirements now encourage facilities to cut power use and carbon emissions. LEDs make compliance simple — delivering high output with low consumption.
Looking ahead, LED lighting will become the backbone of smart, data-driven facilities, where lighting systems communicate with HVAC, security, and production networks.
Ceramiclite’s HB01 High Bay LED bay lights are engineered with these innovations in mind — combining optical precision, smart compatibility, and industrial-grade durability. They’re ready for today’s efficiency demands and tomorrow’s intelligent infrastructure.
Want to know more about What is New in Industrial LED Lighting?
Conclusion
Choosing between high bay vs low bay lighting comes down to three key factors — ceiling height, beam angle, and brightness needs. High bay lights deliver powerful, focused illumination for tall spaces, while low bay lights provide softer, wider coverage for lower ceilings.
Upgrading to LED bay lighting ensures higher efficiency, lower maintenance, and long-term ROI — a smart move for any modern facility.
¿Aún no sabes qué opción se adapta mejor a tu espacio? Solicita hoy mismo un diseño de iluminación gratuito a Ceramiclite y descubre el equilibrio perfecto entre rendimiento, ahorro y fiabilidad para tu entorno industrial.
_thumb.jpg)